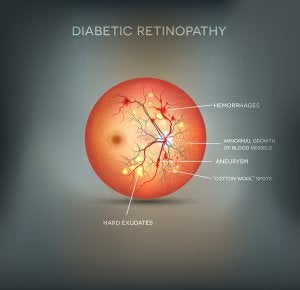
 Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to complications that affect many different parts of the body, including the eyes. This is one reason why it’s essential for patients with diabetes to schedule regular exams with an eye doctor. An ophthalmologist near Chicago can detect diabetic retinopathy when it is still in its early stages. Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that involves damage to the blood vessels of the eyes. Over time, patients may suffer from permanent vision loss.
Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to complications that affect many different parts of the body, including the eyes. This is one reason why it’s essential for patients with diabetes to schedule regular exams with an eye doctor. An ophthalmologist near Chicago can detect diabetic retinopathy when it is still in its early stages. Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that involves damage to the blood vessels of the eyes. Over time, patients may suffer from permanent vision loss.
Identifying the Symptoms
When diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, the ophthalmologist will ask the patient about his or her symptoms. Although this condition does not usually cause symptoms in its early stages, patients may eventually notice blurry vision, spots or floaters in the visual field, dark areas in the visual field, or vision loss. Over time, patients develop an increasing reliance on vision correction, such as eye glasses.
Conducting Diagnostic Exams
In addition to assessing the patient’s symptoms, the ophthalmologist will conduct a comprehensive eye exam. This includes visual acuity measurements to assess whether the central vision is affected. A refraction exam lets the ophthalmologist know if the patient’s prescription has changed. The eye doctor will measure the intraocular pressure. Additionally, the ophthalmologist will conduct a dilated eye exam to examine the structures of the eyes for abnormalities. These can include abnormal blood vessels, swelling or deposits in the retina, bleeding in the vitreous, or the growth of scar tissue and new blood vessels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
One of the goals of treatment for patients with diabetic retinopathy involves slowing or halting the progression of vision loss. To accomplish this, it’s necessary for patients to manage their blood sugar levels properly. A primary care physician can help patients manage their disease through prescription medications, dietary guidelines, and exercise recommendations.
Undergoing Eye Surgery
If diabetic retinopathy is already in the advanced stages, patients may require eye surgery. One option is focal laser treatments, also known as photocoagulation. This procedure involves targeting the abnormal, leaky blood vessels with a laser to seal them. Scatter laser treatments, also known as hand retinal photocoagulation, is similar; however, this procedure can shrink the abnormal blood vessels. A third option is a vitrectomy. For a vitrectomy, the ophthalmologist makes a tiny incision, through which he or she can remove accumulated blood and scar tissue.