Glaucoma refers to a cluster of eye diseases that inflict damage on the optic nerve, resulting in vision loss and perhaps blindness. Glaucoma is typically characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which can occur when fluid accumulates within the eye instead of being drained away. The optic nerve can sustain damage when this pressure builds up. Although glaucoma is a serious eye disease, the good news is that your ophthalmologist can detect it early and recommend effective treatment options to manage the problem. You can facilitate early detection of glaucoma by scheduling a screening at an optical center in Chicago. 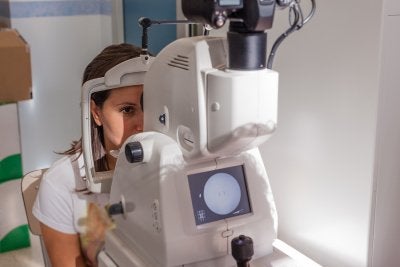
Why You Should Get Screened
Many adults resist going to an ophthalmologist for an eye exam because they think that their vision is fine or that their prescription hasn’t changed. But in fact, eye diseases can develop without causing noticeable symptoms. Only a comprehensive eye exam at an optical center can lead to an accurate diagnosis. Taking an hour or so out of your day to undergo a glaucoma screening is a worthwhile investment in your health. Another important reason why you should get screened is that when left untreated, glaucoma can gradually rob you of your eyesight. When detected and treated early on, glaucoma is quite manageable.
When You Should Get Screened
The reason why it’s important to get screened at age 40 is because this is the time of life when eye diseases and other problems typically begin to develop. Even if your vision appears to be perfect, you could be developing asymptomatic problems like glaucoma. Your ophthalmologist will recommend a glaucoma screening schedule for you to follow. Generally, it’s recommended that patients ages 40 through 54 have a screening every one to three years. Those who are 54 to 64 should have one every one to two years and those who are older than 64 should have one every six to 12 months. Your ophthalmologist may adjust this schedule depending on your specific risk factors of glaucoma.
What Your Risk Factors Might Be
Ask your ophthalmologist if you’re at an increased risk of glaucoma. You may be if you have a family history of the disease, you’re age 40 or older, you have high intraocular pressure, or you are farsighted. People with diabetes, high blood pressure, a history of eye injuries, and a history of corticosteroid use are also at an increased risk.

