-
Treating Age-Related Presbyopia with Eye Surgery
Presbyopia is a vision change that occurs with age. This condition causes problems with focusing on close work, which can be particularly problematic for individuals who work on computers and those who enjoy reading. If you’ve discovered that your contact lenses or eyeglasses are no longer sufficient for your vision, it’s time to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist near Chicago. An ophthalmologist may recommend eye surgery to correct your presbyopia .
As you’ll learn when you watch this video, vision correction for patients with presbyopia may involve the insertion of intraocular lenses (IOLs). This involves removing the natural lens of the eye and replacing it with a synthetic lens. Another possibility is refractive surgery. Your ophthalmologist can reshape your cornea to improve your vision.
-
A Look at the Different Types of Intraocular Lenses
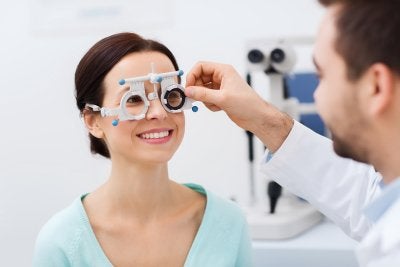
Intraocular implants may be appropriate for some patients with cataracts or presbyopia. When you visit an optical center in Chicago to discuss having this type of eye surgery , the ophthalmologist will explain the different types of intraocular lenses (IOLs) that are available. One popular option is the monofocal lens, which is designed to provide optimal vision at near, intermediate, or far distances. If your monofocal lens is set for near distance, then you would need eye glasses to see at far distances. Another option is to set one lens for near and another for far distances. This is known as monovision and it provides vision at intermediate distances.
Alternatively, your ophthalmologist might recommend that you have multifocal or accommodative lenses. This is a newer type of IOLs that may reduce your dependence on glasses and contact lenses. A multifocal lens features a series of different focal zones, which can allow for both near and far distance vision.

-
Taking Care of Your Eyes as You Age
Did you know that September has been designated as Healthy Aging Month? Its purpose is to remind people that it’s never too late in life to take control of their wellness. One commonly overlooked aspect of aging is its impact on your eyes. Visiting an ophthalmologist in Chicago regularly is important at every stage of life, but it’s particularly crucial as you grow older. Millions of Americans face blindness because of age-related vision changes. Scheduling a comprehensive exam every year with your eye doctor will help you manage your vision health. Not only can your ophthalmologist diagnose problems early on, but he or she can also provide some general eye care tips to help you protect your sight.
Kick the Habit
Your ophthalmologist might advise you to quit smoking. If you smoke, you should know that the habit directly increases your risk of developing cataracts and age-related macular degeneration. Tobacco use can also indirectly increase your risk of vision problems, such as by making you more susceptible to cardiovascular diseases that affect the health of your eyes. Quitting smoking is hard, but dealing with the health consequences of smoking is far worse. By quitting, you’ll improve the health of everyone around you as well as your own health. If you’re having trouble quitting or you need a little more convincing, your eye doctor may refer you to your primary care physician, who can connect you with appropriate resources in your community.
Pay Attention to Your Diet
When you were younger, you might have consumed sugary sodas and baked goods without a second thought, but the body of an older adult is less forgiving. You may have already realized that eating healthier is better for your energy levels, mood, and cardiac health, but it’s also good for your eyes. Certain foods are rich in the nutrients that your eyes need. These include cold water fish like salmon and tuna, dark green leafy vegetables like kale and spinach, and citrus fruits like kiwi and oranges. Eggs are also good for eye health because they contain lutein and zeaxanthin. These nutrients may offer some protection against age-related macular degeneration.
Manage Your Medical Conditions
If you’re undergoing regular wellness exams at your doctor’s office, then you might already know if you have high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, or high glucose levels. If so, it’s important to work with your doctor to manage these problems because they can affect your eye health.
-
The Importance of Glaucoma Screening at Age 40
Glaucoma refers to a cluster of eye diseases that inflict damage on the optic nerve, resulting in vision loss and perhaps blindness. Glaucoma is typically characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which can occur when fluid accumulates within the eye instead of being drained away. The optic nerve can sustain damage when this pressure builds up. Although glaucoma is a serious eye disease, the good news is that your ophthalmologist can detect it early and recommend effective treatment options to manage the problem. You can facilitate early detection of glaucoma by scheduling a screening at an optical center in Chicago.
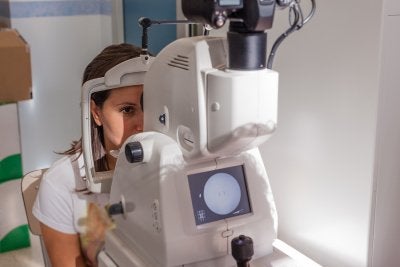
Why You Should Get Screened
Many adults resist going to an ophthalmologist for an eye exam because they think that their vision is fine or that their prescription hasn’t changed. But in fact, eye diseases can develop without causing noticeable symptoms. Only a comprehensive eye exam at an optical center can lead to an accurate diagnosis. Taking an hour or so out of your day to undergo a glaucoma screening is a worthwhile investment in your health. Another important reason why you should get screened is that when left untreated, glaucoma can gradually rob you of your eyesight. When detected and treated early on, glaucoma is quite manageable.
When You Should Get Screened
The reason why it’s important to get screened at age 40 is because this is the time of life when eye diseases and other problems typically begin to develop. Even if your vision appears to be perfect, you could be developing asymptomatic problems like glaucoma. Your ophthalmologist will recommend a glaucoma screening schedule for you to follow. Generally, it’s recommended that patients ages 40 through 54 have a screening every one to three years. Those who are 54 to 64 should have one every one to two years and those who are older than 64 should have one every six to 12 months. Your ophthalmologist may adjust this schedule depending on your specific risk factors of glaucoma.
What Your Risk Factors Might Be
Ask your ophthalmologist if you’re at an increased risk of glaucoma. You may be if you have a family history of the disease, you’re age 40 or older, you have high intraocular pressure, or you are farsighted. People with diabetes, high blood pressure, a history of eye injuries, and a history of corticosteroid use are also at an increased risk.
